You use this program to view the accumulated material and operation costs for any parent part against which a structure is defined.
This program can be run at any time.
If you are new to this query, then the following information will help you achieve the best results:
-
If you know the stock code, then you can enter it directly and press the Tab or Enter key to view the information.
If you do not know the stock code, then you can use the browse function to locate the code.
-
You can personalize this query in a number of ways. These include:
- setting preferences that affect what information is displayed. These settings can be retained for future use
- configuring property sheets (e.g. the section headed Stock Details). This includes being able to sequence items by dragging them up or down, to show important items first
- configuring the Operations and Components listviews. This includes being able to sequence columns by dragging them left or right, sorting columns and changing column widths
- configuring the layout of the panes on the screen, including hiding or displaying panes
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Options | |
| Preferences | Select this to indicate the default criteria for viewing material and operation costs for the item. |
| Stock code | Indicate the stock item for which you want to view material and operation costs. |
| Route | Indicate the route for which you want to view material
and operation costs for the selected item. This defaults to the routing selected in the preferences, but can be changed. This only applies when the option: Alternate routings required is enabled (Bill of Materials Setup). |
This screen is displayed when you select the Preferences option from the Options menu.
| Field | Description | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Save | Select this to save your settings against your operator code. If you do not save your preferences, then your selections are only applied for the current run of the program. | ||||||
| Close | Select this to apply the preferences for the current run of the program only. | ||||||
| Routing |
|
||||||
| Use route on warehouse | Select this to use the route defined against the default warehouse to use for the item (Browse on Warehouses). | ||||||
| Select route | Indicate the default routing to use for the query. This only applies if you did not select to use the route on the warehouse. | ||||||
| Cost basis | |||||||
| Cost selection | Indicate on which costs you want to base
query.
|
||||||
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Stock code | This indicates the code of the stock item you are currently querying. |
| Description |
This indicates the description assigned to the stock item. If neither structures nor operations are held against the item for the route selected, then the description: No components or operationsis displayed. |
| Warehouse |
This indicates the Default warehouse to use defined against the item (Stock Code Maintenance). If you selected Costing by Warehouse (Inventory Setup - General tab), then you can enter the warehouse for which you want to view the costs for the stock item. |
| Use route on warehouse | This indicates whether the route defined against the default warehouse to use for the item (Browse on Warehouses) is being used for the query. |
| Rev/Rel |
This indicates the revision and release for an ECC controlled item. You can select this field to use the ECC History program to indicate a different revison/release to query. |
| Economic batch quantity |
This indicates the EBQ defined against the stock item (Stock Code Maintenance). For a co-product, this is calculated as: EBQ of notional part x total quantity of notional part. |
| Notional parent |
This is displayed if the item is a co-product attached to a notional part. It indicates the code of the notional parent part to which the co-product is attached (see BOM Co-products). |
| Links |
|
| ABC elements | This is only displayed if you selected the option: ABC costing required (Bill of Materials Setup) and elements of cost (i.e. at pre-production, manufacturing or sales level) have been assigned to the item. |
The following information is included in this pane:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Actual costs |
These are the costs held against the stock item (if the Costing per warehouse inventory setup option is not enabled) or the cost held against the warehouse (if the Costing per warehouse and the Apply warehouse BOM costs inventory setup options are enabled). See also Costing Report - Report Details. |
| Calculated costs | Refer to Fixed and Variable Overhead Calculations. |
Following are examples of Calculated costs for fixed and variable costs.
This section uses an example to describe how the Fixed and Variable overhead costs are calculated with progressive scrap.
Assume you have a stock code with the following:
| Setup Time 15 | Rate 0.4684 |
| Run Time .75 | Rate 0.4684 |
| Fixed Overhead | Rate 0.4441 |
| Variable Overhead | Rate 0.4770 |
| Productive Unit 1 | |
| EBQ 500 | |
| 10% Progressive scrap |
-
You use the following calculation to calculate the Starting Quantity to make one of the parent:
Starting quantity = End quantity / (1 – (Scrap % / 100))
Starting quantity = 1 / ( 1 – 0.1 )
Starting quantity = 1 / 0.9
Starting quantity = 1.111
-
Calculating the new run time including progressive scrap:
The Run Time is 0.75 to make one of the parent
Progressive scrap included is 0.75 x 1.111 = 0.83333
New run time = 0.8333
The following key applies to the formulas:
EBQ - Economic Batch Quantity
STQ - Startup Quantity
STT - Startup Time
PU - Productive Unit
RT - Run Time
SUT - Set-up Time
TDT - Tear Down Time
-
Unit Fixed Overhead Value
This is calculated as:
{[(SUT x PU)+(STT x PU)+((EBQ - (STQ x PU)) x RT)+(TDT x PU)] x Rate} / EBQ
Using the example we have:
{[(15 x1)+(0 x 1)+((500 - (0x 1)) x 0.83333)+(0 x 0)] x 0.4441 } / 500
= {[(15)+(0)+((500 - (0) x 0.83333)+(0)] x 0.4441} / 500
= {[(15+416.665)] x 0.4441} / 500
= {431.665 x 0.4441} / 500
= 191.7024265 / 500
Fixed Rate Cost = 0.38341 (0.383404853)
-
Unit Variable Overhead Value
{[(SUT x PU)+(STT x PU)+((EBQ - (STQ x PU)) x RT)+(TDT x PU)] x Rate} / EBQ
Using the example we have:
{[(15 x1)+(0 x 1)+((500 - (0x 1)) x 0.83333)+(0 x 0)] x 0.4770} / 500
= {[(15)+(0)+((500 - (0) x 0.83333)+(0)] x 0.4770} / 500
= {[(15+416.665)] x 0.4770} / 500
= {431.665 x 0.4770} / 500
= 205.904205 / 500
Variable Rate Cost = 0.41181 (0.41180841)
![[Note]](images/note.png)
If you have more than one operation you have to start the calculation from the last Operations first.
This section explains how costing is calculate for a work center defined with a Run time calculation method of Block.
When the work center is defined as a Block type, each ‘run’ always consumes a block of time. Therefore, if the EBQ is 1749 and the operation can produce 2,000 of the parent every three hours, then this operation will take 3 hours to produce 1749 units.
To calculate the unit run time, divide 3 by 1749 giving a calculated run time of 0.0017 hours per unit.
This produces the following data:
| Variable | Time | Rate | Formula | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run time | 0.0017 | 20 | (Hours x Rate x EBQ) / EBQ | 0.03400 |
| Teardown | 0.5833 | 15 | (Hours x Rate x PUnit) / EBQ | 0.00500 |
| Setup | 0.1660 | 20 | (Hours x Rate x PUnit) / EBQ | 0.00190 |
| Fixed overhead | Operation time | 15 | (Rate x ((RunHr x EBQ) + (SetHr x PUnit) +(TearHr x PUnit))) / EBQ | 0.03193 |
| Variable overhead | Operation time | 10 | (Rate x ((RunHr x EBQ) + (SetHr x PUnit) + (TearHr x PUnit))) / EBQ | 0.02128 |
The Overhead values are reported individually. The other values are summed into labor. Therefore labor is 0.034 + 0.005 + 0.0019 totalling to 0.0409.
There are some other factors in these formulas, but for simplicity only the relevant fields are used.
![[Note]](images/note.png)
|
|
|
Although the calculations are done to 6 decimal places, potential rounding errors can still occur. The unit of time must therefore be carefully defined. |
|
Operation costs are established by accumulating the results of the following calculations (see also Fixed and Variable Overhead Calculations):
- If the productive units are zero, then 1 is assumed.
-
If the economic batch quantity is less than the startup quantity x productive units, then the startup quantity x productive units is used as the economic batch quantity.
-
If the economic batch quantity is less than one, then 1 is assumed.
An EBQ of 0 to 1 will have the same setup value.
The setup time is the time taken to set up the machinery, etc., for use. If the EBQ is greater than 1, then the setup value can be distributed according to the EBQ. However if the EBQ is less than 1, it still only costs the equivalent of an EBQ of 1 in setting up.
-
For subcontracted operations, the subcontracted unit value is accumulated as a material cost onto the parent part.
![[Note]](images/note.png)
The Productive Units are taken from the Operation against the Bill of Materials (Structures and Routings - Maximum units field of the Operation) and not from the Work Center.
Run value (run time x run rate x (EBQ - (startup quantity x productive units))) / EBQ Setup (setup rate x setup time x productive units) / EBQ Startup (startup rate x startup time x productive units) / EBQ Teardown (teardown rate x teardown time x productive units) / EBQ Fixed overhead (fixed overhead rate x ((run time x (EBQ - (startup quantity x productive units))) + (setup time x productive units) + (startup time x productive units) + (teardown time x productive units))) / EBQ Variable overhead (variable overhead rate x ((run time x (EBQ - (startup quantity x productive units))) + (setup time x productive units) + (startup time x productive units) + (teardown time x productive units))) / EBQ The reason for including the EBQ (Economic Batch Quantity) in the costs is that the EBQ is the optimum batch quantity to produce from a costing point of view and is thus applied when determining your standard unit labor costs. Applying the economic batch quantity (EBQ) gives an accurate standard unit labor cost based on the optimum production quantity.
If, for example, you produce an item in quantities of 10 as a rule, then your setup cost would be shared by each unit of the item. Having a setup cost ignoring the EBQ would reflect an inflated standard unit setup cost and therefore an inflated overall standard unit labor cost.
-
Cost %
For a co-product, this indicates the co-product's percentage material cost of the notional part.
Material costs (cost of components) are established by accumulating the results of the following calculations:
- The quantity per is increased by the scrap percentage factor, and by the result of dividing the scrap quantity by the economic batch quantity.
-
Multiply the cost of each first level component by its recalculated quantity per and add the costs of all the operations on the part.
If the economic batch quantity is zero the program automatically assumes a quantity of 1.
- If you defined a fixed quantity per against a component (Structures and Routings), then no progressive scrap calculations are applied to that quantity (the fixed quantity per is always calculated according to the net quantity to make).
-
Soft phantoms
Operation costs of soft phantom components (Inventory Setup) are not included in the cost of the parent.
The BOM Costing Query emulates how the cost implosion works in that the EBQ is used as a basis to calculate the UNIT cost of an item.
For example, you have a parent item with an EBQ of 100 which has a component with a fixed quantity of 1 @ 2,500.00.
The costing query and, by extension, the BOM cost implosion, assumes that you manufacture by EBQ and therefore the apportionment of the cost of the component is 2,500 / 100 = 25.00 per item.
The following information is included in this listview:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| W/h |
This indicates the warehouse to use for the component. This can be the warehouse defined against the structure. If this is not defined, then it is the component warehouse to use defined against the control record of the parent warehouse. If neither of these is defined, then it is the component's warehouse to use (Stock Code Maintenance). |
| Cost % | For a co-product, this indicates the co-product's percentage material cost of the notional part. |
| ECC consumption | The ECC consumption method for an ECC controlled item is displayed. |
-
If you last ran the Cost Implosion program based on a range of stock codes, then a warning message indicates that your BOM costs may be incorrect. For accurate costing you must run the Cost Implosion program using all stock codes.
If the option: Warn about cost implosion not being completed is selected (Bill of Materials Setup - General tab) then the message: BOM costs may be incorrect due to last implosion run. OK to continue? is displayed when the Cost Implosion was not run for all stock codes and warehouses. This merely indicates that the costs of the excluded items may not be correct.
-
Costs are shown in terms of the (EBQ) Economic Batch Quantity. If the EBQ is not defined, then the costs are shown in terms of one parent part.
-
Costs are calculated from one of the following:
-
the cost held against the stock item (Stock Code Maintenance - Other tab)
OR
- the cost held against the warehouse (Warehouses for Stock Code) if you selected the option: Apply warehouse BOM costs and you selected Costing by warehouse (Inventory Setup -General tab).
-
-
To prevent rounding differences in costs between the various costing programs (e.g. Inventory Query cost analysis, Costing Query and Costing Report) you should run the Cost Implosion together with the option: Update unit run times enabled.
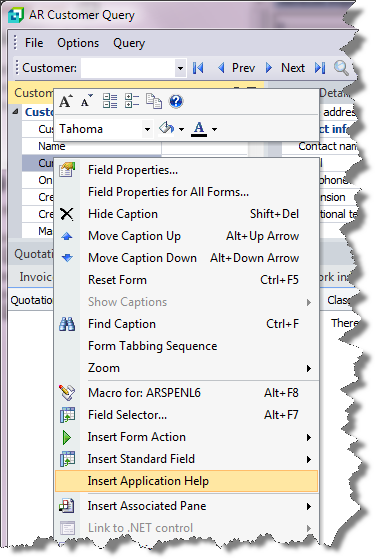
Inserting Application Help
You would typically follow this procedure to display help for the current program in a customized pane that can be pinned to the program window.
Information includes step-by-step instructions for the various functions available within the program, including a brief overview of what the program does, what setup options are required and how to personalize the program.
-
Open the program for which you want to insert application help into a customized pane.
This functionality is only available for a program that has panes.
-
Right-click any form field.
You can also click the triangle menu icon that appears in the title area of a pane.
-
Select Insert Application Help from the context-sensitive menu.
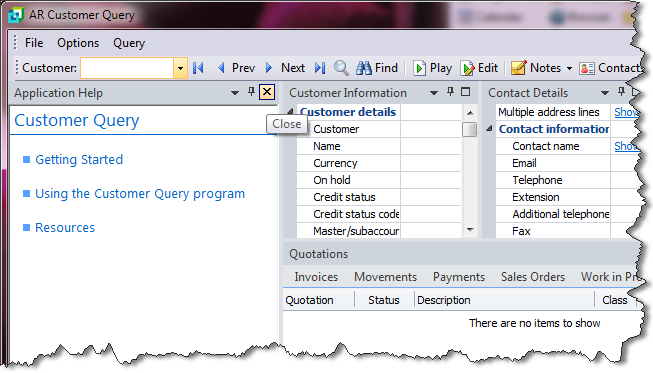
The application help appears in a pane within your program. You can reposition the pane using the docking stickers or pin it to the program window.
Removing the Application Help pane
If you no longer want to display application help in a pane for your current program, you can simply remove it.
-
Select the Close icon in the right-hand corner of the application help pane.
-
Confirm that you want to delete the pane.