You use this program to maintain the integrity of data in your Accounts Receivable module, to close the current month and open up a new month for processing your accounts receivable transactions and to delete accounts receivable information that is no longer required in the system.
This is achieved through the following functions:
- Balance
- Month end
- Year end
- Purge
- AR Period End
- Information
- Report
- Balance
- Month End
- Year End
- Purge
- Error Messages
- Invoice Ageing
- Credit Status
- Balance Brought Forward
- Notes and warnings
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Start Processing | Select this to begin processing the function you selected. |
| Select this to print the information currently displayed in the Report pane. | |
| Save Form Values | This option is only enabled in Design mode (see Automation Design). Your selections are saved and applied when the program is run in automated mode. |
| Field | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control details | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current month number | This indicates the current month number of your Accounts Receivable module. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period end date | This indicates the period end date for the current month as defined on the Periods tab of the Accounts Receivable Setup program. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Processing options | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function | This enables you to indicate the processing function
you want to perform.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset customer credit status |
Select this option to reset the credit status held against customers.
Refer to Credit Status for information on how a customer's credit status is determined. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset lowest unprocessed journal |
Select this to locate the earliest Accounts Receivable journal that has not been posted. The AR Invoice GL Integration and AR Payments GL Integration programs create and/or post General Ledger journals from Accounts Receivable sales and payment transaction journals according to your General Ledger Integration settings. The AR Invoice GL Integration and AR Payments GL Integration programs use the lowest unprocessed Accounts Receivable sales and payment transaction journal numbers as a starting point to create/post these General Ledger journals. Selecting this option therefore ensures that no Accounts Receivable journal is skipped when the General Ledger journals are created/posted for the Accounts Receivable module. This option is only available when you select to process a Balance function.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Date entry | The date selected/entered is used to:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Run date | You use this field to indicate the processing date for the selected function. By default, the Run date is the Company date, but this can be changed when you select to process a Month end or a Year end or you select the Reset customer credit status option and you select the Date entry > Manual date option.The date entered here is used to:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Day of month | Indicate the day for processing which you require. Only the day of the Run date is changed to the day indicated here, leaving the month and year currently displayed. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| After processing completed | These options are displayed within programs that can be automated. They enable you to indicate the action you want to perform once processing is complete (see Automation Design). | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Purge details | These details relate only to the Purge function and are
displayed for information purposes only. Refer to Purge for additional information. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
The information in this pane is displayed once processing is complete, providing you did not select the option: After processing completed > Close this application.
The results of processing the function you selected are displayed.
You use the After processing completed options to print or email this information.
The system performs the following routine for a Balance:
-
For each customer invoice, the current balance is recalculated from the original invoice amount plus any payment transactions made against the invoice.
If there is any change to the current balance, a line is printed for the invoice indicating that a change has been made.
In addition, the next payment number for each invoice is recalculated based on the number of payments on file for the invoice.
-
For each customer, the current balance is recalculated from the sum of the current balances of the invoices on file as follows:
All outstanding invoice are added up for the customer and compared to the customer's balance. When a difference is found, the current customer balance is adjusted to equal the sum of the invoices. A balance correction line is printed indicating the customer to which the change was made.
All customer balances are then accumulated to give the AR Control balance.
-
The aged balances held against each customer are updated. These balances can be viewed within the Customer Query program.
Refer to Invoice Ageing for examples of how aged balances are calculated.
-
The current Accounts Receivable balance on the control record is recalculated from the sum of the current balances of all customers on file.
If there is any change to the current Accounts Receivable balance, a line is printed indicating that a change has been made, and the change made is added to the control record month-to-date balance corrections field.
-
For each customer, the average number of days it takes the customer to pay an invoice is recalculated. This is determined by dividing the total number of zero balance invoices against each customer into the total number of days it took to pay those invoices.
An invoice/debit note is included in the calculation if:
- the invoice balance is zero
- the last transaction against the invoice was a payment
- the transaction amount was less than zero (i.e. it was not a payment reversal)
- the transaction posting year and month is not earlier than the cut off year and month determined from the number of months to use the average days to pay calculation (Accounts Receivable Setup - History tab).
If an invoice/debit note meets all these criteria, then the difference in days is calculated between the transaction journal date and the invoice date.
The total number of zero balance invoices included in the calculation and the total age of all zero balance invoices included in the calculation are stored for each customer and used to calculate the average days to pay. The average days to pay value can be viewed in the Sales Order Entry and Customer Query programs.
-
For each customer, the age of the oldest invoice with a positive balance is calculated and saved together with the applicable invoice number against the customer. Depending on which options are selected, these fields may be used when credit checking is performed or when running the Credit Management report.
The oldest invoice is calculated by determining the difference in days between the Run date and each invoice date until the oldest invoice is established.
![[Note]](images/note.png)
If the Invoice ageing method is By invoice due date (Accounts Receivable Setup – General tab) then the difference in days between the Run date and each invoice date is reduced by the due days against the terms code attached to the invoice.
-
If you selected the option: Reset customer credit status, then invoices are aged into buckets to establish the highest bucket with a positive balance. This then corresponds to a credit status, which is saved against the customer (Browse on Customers – General 2 tab). Depending on which options are selected, the credit status may be used when credit checking is performed or when running the Credit Management report or the Credit Letter Extract program.
Refer to Credit Status for information on how a customer's credit status is determined.
-
For all customer invoices, if an invoice has a zero balance, but the tax portion of the invoice is not zero, then the tax portion of the invoice is set to zero.
The system performs the following routine for a Month end:
-
The 24 months sales figures on each customer record are rolled one month.
The month-to-date sales value for the customer is copied to the previous month 1 sales value.
-
All month-to-date values for each customer are reset to zero.
-
The credit status for each customer is reset.
Refer to Credit Status for information on how a customer's credit status is determined.
-
The aged balances held against the customer are updated.
Refer to Invoice Ageing for information on how the aged balances for a customer are determined.
-
For all customer invoices, if an invoice has a zero balance, but the tax portion of the invoice is not zero, then the tax portion of the invoice is set to zero.
-
If you enabled the option: Consolidate brought forward customers at month end (Accounts Receivable Setup) then the invoices of each balance forward customer are sorted into buckets according to their age, based on the ageing method. For each group of invoices, the invoice balance for the current and two previous periods and the original discount amount are accumulated. All original invoices and their associate payments, adjustments, credit notes, debit notes, invoice and POD multimedia and POD notepad notes are then deleted (see Balance Brought Forward).
A new single invoice is then created for each aged bucket, with an asterisk (*) as the first character of the invoice number followed by a number, starting from 00001 upwards. Each aged bucket is associated with one of the last seven statement dates and the invoice date is set to the applicable statement date. The accumulated discount amount and invoice balances are written to the new invoice. The original invoice amount on the new invoice is also updated with the accumulated invoice balance for the current month.
![[Note]](images/note.png)
-
Reports that print detailed information on invoices and the transactions processed against them (e.g. AR Trial Balance, Statement Print and Credit Management) will only report on the consolidated invoices once the month end has been processed.
-
Invoices for foreign currency customers are not consolidated, because each invoice can have its own fixed exchange rate.
-
Future invoices (i.e. invoices that have an invoice date in the future) are not consolidated.
-
-
Permanent entries that have not expired have their posted this month indicator reset to N.
-
The Accounts Receivable control record is updated as follows:
- If you enabled the option: Close previous month automatically (Company Maintenance) then the current month is set to a status of closed, otherwise the second previous month is set to a status of closed.
- The entered Run date is moved to the month end date for the current financial month.
- The current financial month number is incremented by one.
- The current financial month is set to a status of open.
- All month-to-date values on the control record are reset to zero.
- The current balance is moved to the balance forward.
-
The period-to-date and month-to-date taxable, tax exempt, and tax amounts on the tax control records in the company tax control file are reset to zero.
The system performs the following routine for a Year end:
-
All the month end steps are processed.
-
For each customer, the year-to-date sales and profit fields are set to zero after the figures therein have been moved to the previous year-to-date sales and profit fields.
-
The Accounts Receivable control record is updated as follows:
- the current financial month number is reset to 1
- the current financial year is incremented by 1
- the current year's next cash posting journal number, next invoice register number, month end dates and open/closed flags are moved to the previous year
- the next cash posting journal number and invoice register for the current year are set to 1
- the current year's month end dates are all set to zero
- the first month of the year (which is now the current month) is set to a status of open
-
The year-to-date taxable, tax exempt, and tax amounts on the tax control records in the company tax control file are reset to zero.
A purge can be run together with either a month end or year end, or as a separate process.
The system performs the following routine when doing a Purge:
-
Ledger distribution records are processed as follows if Accounts Receivable is linked to General Ledger in detail or summary (General Ledger Integration):
-
Sales entries are deleted if they meet the following conditions:
- the General Ledger journals for all sales transactions have been created (AR Invoice GL Integration)
- the General Ledger journals created for the sales transactions have been posted (GL Journal Entry)
-
the number of ledger periods for which sales transaction records are being retained (Accounts Receivable Setup - History tab) is exceeded.
![[Note]](images/note.png)
The current month is not included in the calculation that determines the retention period.
-
Payment entries are deleted if they meet the following conditions:
- the General Ledger journals for all payment transactions have been created (AR Payments GL Integration)
- the General Ledger journals created for the payment transactions have been posted (GL Journal Entry)
-
the number of ledger periods for which payment history is being retained (Accounts Receivable Setup - History tab) is exceeded.
![[Note]](images/note.png)
The current month is not included in the calculation that determines the retention period.
-
-
Permanent entries are deleted from the file once the entry is expired. Temporary entries are deleted from the file once the entry has been posted. (see AR Permanent Entry Maintenance)
-
All customer notes are deleted for customers no longer held on file. Similarly, all invoice notes are deleted for invoices no longer on file.
-
Customer movements are processed as follows:
- If you are retaining movement records by date, then the number of days between the current system date and each movement date is compared to the maximum number of days you are retaining records. If a movement record is older than the number of days, it is removed.
- If you are retaining movement records by number, then for each stock code/warehouse combination the number of movement records is counted. If the number of records exceeds the number of records you are retaining, the excess records starting from the oldest movement forward are deleted.
-
Invoices that reach a zero balance in a financial month and year before the cut-off date specified, are removed. Payment details for these invoices in the payment detail file are also removed.
-
Payment journals are deleted if they match the following conditions:
- the journal has been printed.
- the journal was posted in a financial month and year prior to the cut-off month and year.
- if the bank deposit slip is required, then the deposit slip for the journal must have been printed.
- if the Interface module is installed and exports are required, then the journal must either have been exported, or the age of the journal (compared to the current system date) must exceed the maximum number of days you are retaining records before automatic deletion.
-
Any payment history records that were created in a financial month and year before the cut-off date specified, are removed.
If you selected to print discount credit and debit notes (Accounts Receivable Setup - Terms Discount tab), then discount credit and debit note records are deleted if they are older than the specified number of months specified to retain discount notes (Accounts Receivable Setup - History tab).
-
Sales transaction records are processed as follows:
![[Note]](images/note.png)
Records are written to the sales transaction file each time an invoice is created within either the Accounts Receivable or Sales Order modules.
For each invoice detail line, the following records are written to the file:
- a detail sales transaction record (referred to as a D record)
- a Canadian GST tax record, if Canadian GST is in use (referred to as an F record)
For each invoice, the following records are written to the file:
- an invoice summary record (referred to as an S record)
- a foreign invoice summary record, if Foreign currency sales is in use (referred to as an s record)
- a tax summary record (referred to as a T record)
-
Invoice detail records (type D)
- the financial month and year in which the invoice was created must be less than the cut-off month and year for the detail records.
- if Accounts Receivable sales are integrated to General Ledger, then all General Ledger journals for sales transactions must be created (AR Invoice GL Integration)
- if the Activity Based Costing module is installed and the record is for a stocked merchandise line, then all the General Ledger journals for sales transactions must have been created (AR Invoice GL Integration).
- if the Sales Analysis module is installed, then the Sales Analysis Update program must have been run. This updates the sales by salesperson, sales by product class, and sales history files.
- if the Interface module is installed and exports are required, then the detail record must either have been exported, or the invoice date of the record (compared to the current system date) must exceed the number of days you are retaining records before automatic deletion.
-
Invoice summary records (type S)
- the financial month and year in which the invoice was created must be less than the cut-off month and year for the summary records.
- the General Ledger journals for sales transactions must have been created (AR Invoice GL Integration).
- if the Sales Analysis module is installed, then the Sales Analysis Update program must have been run. This updates the sales commission and tax files.
- if the General Ledger module is installed and a global tax file is required, then the global tax file must have been updated from the invoice.
- if the Interface module is installed and exports are required, then the detail record must either have been exported, or the invoice date of the record (compared to the current system date) must exceed the number of days you are retaining records before automatic deletion.
-
Foreign invoice summary records (type s)
- the financial month and year in which the invoice was created must be less than the cut-off month and year for the summary records.
- the General Ledger journals for sales transactions must have been created (AR Invoice GL Integration).
- if the Interface module is installed and exports are required, then the detail record must either have been exported, or the invoice date of the record (compared to the current system date) must exceed the number of days you are retaining records before automatic deletion.
-
Canadian GST records (type F)
- if the Sales Analysis module is installed, then the Sales Analysis Update program must have been run. This updates the Canadian GST files.
- if the General Ledger module is installed and a global tax file is required, then the global tax file must have been updated from the invoice (by running the Invoice Register).
- if the Interface module is installed and exports are required, then the detail record must either have been exported, or the invoice date of the record (compared to the current system date) must exceed the number of days you are retaining records before automatic deletion.
-
Tax summary records (type T)
- if Accounts Receivable sales are integrated to General Ledger (General Ledger Integration) and sales tax is integrated to General Ledger at tax code level (Tax Options) then the General Ledger journals for sales transactions must have been created (AR Invoice GL Integration).
- if the Sales Analysis module is installed, then the Sales Analysis Update program must have been run. This updates the sales commission and tax files.
- if the Interface module is installed and exports are required, then the detail record must either have been exported, or the invoice date of the record (compared to the current system date) must exceed the number of days you are retaining records before automatic deletion.
-
A report is printed with a summary for each file processed as follows:
- the number of ledger distribution entries deleted
- the number of expired permanent entries deleted
- the number of customer narrations deleted
- the number of movement records deleted
- the number of zero balance invoices deleted
- the number of cash journals deleted
- the number of payment history records deleted
- the number of sales transaction detail records deleted (type D)
- the number of sales transaction summary records deleted (type S and s) - the number of tax records deleted (type F and T)
The following are error messages which could be printed on the report produced by the Balance function:
-
"acc no" invoice count raised by n (where "acc no" indicates the customer account number and n indicates the value by which the invoice count was raised.
This error occurs when the actual number of invoices found against the customer account number does not agree with the value in the InvoiceCount field of the ArCustomer table/file. The InvoiceCount field is amended.
-
Sub/Ac - No details allowed
This occurs when the system finds invoices against a sub-account, which should be on the master account.
If a sub-account is linked to a master account so that the sub-account's invoices are attached to the master account, there should be no invoices or balances on the sub-account.
The following examples illustrate how the AR Period End program determines the aged balances for each customer, depending on the Invoice ageing method selected (Accounts Receivable Setup - General tab).
The examples are based on the following information:
The run date is 15 August 20xx. The following invoices are attached to the customer's account:
| Invoice Number | Invoice Date | Invoice Terms | Invoice Balance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100650 | 4 September 20xx | 30 days | 25.00 |
| 800098 | 10 August 20xx | 30 days | -30.00 |
| 100570 | 17 July 20xx | 30 days | 29.00 |
| 100568 | 16 July 20xx | 30 days | 30.00 |
| 100557 | 17 June 20xx | 30 days | 59.00 |
| 100554 | 16 June 20xx | 30 days | 60.00 |
| 100550 | 18 May 20xx | 30 days | 89.00 |
| 100480 | 17 May 20xx | 30 days | 90.00 |
| 100460 | 18 April 20xx | 30 days | 119.00 |
| 100458 | 17 April 20xx | 30 days | 120.00 |
| 100420 | 17 March 20xx | 30 days | 151.00 |
| 100400 | 15 February 20xx | 30 days | 181.00 |
Example 1
Invoice ageing method is By statement based on the standard 30 days ageing method according to the period end dates defined in Accounts Receivable and not and using the Number of days fixed option which allows you to define your own ageing buckets. If you are using the Number of days fixed option, then invoices are aged in the same manner as By statement, but according to the period end dates specified against your ageing buckets in the AR Invoice Terms program.
The last seven statement dates are:
| 1 | 30 July 20xx |
| 2 | 30 June 20xx |
| 3 | 30 May 20xx |
| 4 | 30 April 20xx |
| 5 | 30 March 20xx |
| 6 | 28 February 20xx |
| 7 | 30 January 20xx |
The invoices are aged into their appropriate buckets as follows:
- If the invoice date is in the future, then the invoice balance is added to the Future Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 25.00.
- If the invoice balance is negative, then the invoice balance is added to the Credit Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is -30.00.
- If the invoice is less than 30 days old, then the invoice balance is added to the Current Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is -30.00.
- If the invoice is less than 60 days old, then the invoice balance is added to the 30 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is -59.00.
- If the invoice is less than 90 days old, then the invoice balance is added to the 60 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 119.00.
- If the invoice is less than 120 days old, then the invoice balance is added to the 90 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 179.00.
-
If the invoice is 120 days old or more, then the invoice balance is added to the 120 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 571.00.
The following table illustrates this ageing:
Invoice Number Invoice Date Invoice Terms Invoice Balance Age Bucket 100650 4 September 20xx 30 days 25.00 Future Future 800098 10 August 20xx 30 days -30.00 Current Current and Credit 100570 17 July 20xx 30 days 29.00 30 days 30 days 100568 16 July 20xx 30 days 30.00 30 days 30 days 100557 17 June 20xx 30 days 59.00 60 days 60 days 100554 16 June 20xx 30 days 60.00 60 days 60 days 100550 18 May 20xx 30 days 89.00 90 days 90 days 100480 17 May 20xx 30 days 90.00 90 days 90 days 100460 18 April 20xx 30 days 119.00 120 days 120 days 100458 17 April 20xx 30 days 120.00 120 days 120 days 100420 17 March 20xx 30 days 151.00 150 days 120 days 100400 15 February 20xx 30 days 181.00 180 days 120 days
Example 2
Invoice ageing method is By aged statement.
The last seven statement dates are:
| 1 | 30 July 20xx |
| 2 | 30 June 20xx |
| 3 | 30 May 20xx |
| 4 | 30 April 20xx |
| 5 | 30 March 20xx |
| 6 | 28 February 20xx |
| 7 | 30 January 20xx |
The invoices are aged into their appropriate buckets as follows:
- If the invoice date is in the future, then the invoice balance is added to the Future Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 25.00.
- If the invoice balance is negative, then the invoice balance is added to the Credit Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is -30.00.
- If the invoice is less than 30 days old, then the invoice balance is added to the Current Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 29.00.
- If the invoice is less than 60 days old, then the invoice balance is added to the 30 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 119.00.
- If the invoice is less than 90 days old, then the invoice balance is added to the 60 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 179.00.
- If the invoice is less than 120 days old, then the invoice balance is added to the 90 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 239.00.
-
If the invoice is 120 days old or more, then the invoice balance is added to the 120 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 332.00.
The following table illustrates this ageing:
Invoice Number Invoice Date Invoice Terms Invoice Balance Age Bucket 100650 4 September 20xx 30 days 25.00 Future Future 800098 10 August 20xx 30 days -30.00 Current Current and Credit 100570 17 July 20xx 30 days 29.00 Current Current 100568 16 July 20xx 30 days 30.00 Current Current 100557 17 June 20xx 30 days 59.00 30 days 30 days 100554 16 June 20xx 30 days 60.00 30 days 30 days 100550 18 May 20xx 30 days 89.00 60 days 60 days 100480 17 May 20xx 30 days 90.00 60 days 60 days 100460 18 April 20xx 30 days 119.00 90 days 90 days 100458 17 April 20xx 30 days 120.00 90 days 90 days 100420 17 March 20xx 30 days 151.00 120 days 120 days 100400 15 February 20xx 30 days 181.00 150 days 120 days
Example 3
Invoice ageing method is By invoice date.
The number of days between each Invoice Date and the Run Date is determined and the invoices are aged into their appropriate buckets as follows:
- If the invoice date is in the future, then the invoice balance is added to the Future Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 25.00.
- If the invoice balance is negative, then the invoice balance is added to the Credit Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is -30.00.
- If the invoice is less than 30 days old, then the invoice balance is added to the Current Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is -1.00.
- If the invoice is less than 60 days old, then the invoice balance is added to the 30 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 89.00.
- If the invoice is less than 90 days old, then the invoice balance is added to the 60 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 149.00.
- If the invoice is less than 120 days old, then the invoice balance is added to the 90 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 209.00.
-
If the invoice is 120 days old or more, then the invoice balance is added to the 120 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 452.00.
The following table illustrates this ageing:
Invoice Number Invoice Date Invoice Terms Invoice Balance Age Bucket 100650 4 September 20xx 30 days 25.00 Future Future 800098 10 August 20xx 30 days -30.00 5 days Current and Credit 100570 17 July 20xx 30 days 29.00 29 days Current 100568 16 July 20xx 30 days 30.00 30 days 30 days 100557 17 June 20xx 30 days 59.00 59 days 30 days 100554 16 June 20xx 30 days 60.00 60 days 60 days 100550 18 May 20xx 30 days 89.00 89 days 60 days 100480 17 May 20xx 30 days 90.00 90 days 90 days 100460 18 April 20xx 30 days 119.00 119 days 90 days 100458 17 April 20xx 30 days 120.00 120 days 120 days 100420 17 March 20xx 30 days 151.00 151 days 120 days 100400 15 February 20xx 30 days 181.00 181 days 120 days
Example 4
Invoice ageing method is By invoice due date.
The number of days between each Invoice Date and the Run Date is determined and this figure is reduced by the due days against the terms Code attached to the invoice. The invoices are aged into their appropriate buckets as follows:
- If the invoice date is in the future, then the invoice balance is added to the Future Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 25.00.
- If the invoice balance is negative, then the invoice balance is added to the Credit Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is -30.00.
- If the invoice is not yet due, then the invoice balance is added to the Current Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 29.00.
- If the invoice is 1-30 days overdue, then the invoice balance is added to the 30 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 119.00.
- If the invoice is 31-60 days overdue, then the invoice balance is added to the 60 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 179.00.
- If the invoice is 61-90 days overdue, then the invoice balance is added to the 90 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 239.00.
-
If the invoice is 91 days or more overdue, then the invoice balance is added to the 120 Day Invoices bucket. In this example, this bucket's balance is 332.00.
The following table illustrates this ageing:
Invoice Number Invoice Date Invoice Terms Invoice Balance Age Bucket 100650 4 September 20xx 30 days 25.00 Future Future 800098 10 August 20xx 30 days -30.00 Current Current and Credit 100570 17 July 20xx 30 days 29.00 Current Current 100568 16 July 20xx 30 days 30.00 Current Current 100557 17 June 20xx 30 days 59.00 29 days 30 days 100554 16 June 20xx 30 days 60.00 30 days 30 days 100550 18 May 20xx 30 days 89.00 59 days 60 days 100480 17 May 20xx 30 days 90.00 60 days 60 days 100460 18 April 20xx 30 days 119.00 89 days 90 days 100458 17 April 20xx 30 days 120.00 90 days 90 days 100420 17 March 20xx 30 days 151.00 121 days 120 days 100400 15 February 20xx 30 days 181.00 151 days 120 days
The following examples illustrate how the AR Period End program determines a customer's credit status, when you select the option: Reset customer credit status.
The examples are based on the following information:
The run date is 15 August 20xx. The following invoices are attached to the customer's account:
| Invoice Number | Invoice Date | Invoice Terms | Invoice Balance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 800056 | 12 May 20xx | 30 days | -45.00 |
| 100512 | 8 June 20xx | 7 days | 50.00 |
| 100513 | 8 June 20xx | 30 days | 120.00 |
| 100556 | 18 June 20xx | 30 days | 85.00 |
Example 1
Invoice ageing method is By statement.
The last seven statement dates are:
| 1 | 30 July 20xx |
| 2 | 30 June 20xx |
| 3 | 30 May 20xx |
| 4 | 30 April 20xx |
| 5 | 30 March 20xx |
| 6 | 28 February 20xx |
| 7 | 30 January 20xx |
The invoices are aged into their appropriate buckets using the table below:
| 0 | Indicates only current invoice |
| 1 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 30 days old or over |
| 2 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 60 days old or over |
| 3 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 90 days old or over |
| 4 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 120 days old or over |
| 5 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 150 days old or over |
| 6 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 180 days old or over |
The following table illustrates this ageing:
| Invoice Number | Invoice Date | Invoice Terms | Invoice Balance | Age | Bucket |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800056 | 12 May 20xx | 30 days | -45.00 | 90 days | 3 |
| 100512 | 8 June 20xx | 7 days | 50.00 | 60 days | 2 |
| 100513 | 8 June 20xx | 30 days | 120.00 | 60 days | 2 |
| 100556 | 18 June 20xx | 30 days | 85.00 | 60 days | 2 |
In this example the oldest bucket is 3. However, the balance of the bucket is negative so the bucket's balance is taken off the next oldest bucket until the buckets balance is greater than zero. Therefore, the oldest bucket in this example is 2. This makes the customer's credit status 2.
Example 2
Invoice ageing method is By aged statement.
The last seven statement dates are:
| 1 | 30 July 20xx |
| 2 | 30 June 20xx |
| 3 | 30 May 20xx |
| 4 | 30 April 20xx |
| 5 | 30 March 20xx |
| 6 | 28 February 20xx |
| 7 | 30 January 20xx |
The invoices are aged into their appropriate buckets using the table below:
| 0 | Indicates only current invoice |
| 1 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 30 days old or over |
| 2 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 60 days old or over |
| 3 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 90 days old or over |
| 4 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 120 days old or over |
| 5 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 150 days old or over |
| 6 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 180 days old or over |
The following table illustrates this ageing:
| Invoice Number | Invoice Date | Invoice Terms | Invoice Balance | Age | Bucket |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800056 | 12 May 20xx | 30 days | -45.00 | 60 days | 2 |
| 100512 | 8 June 20xx | 7 days | 50.00 | 30 days | 1 |
| 100513 | 8 June 20xx | 30 days | 120.00 | 30 days | 1 |
| 100556 | 18 June 20xx | 30 days | 85.00 | 30 days | 1 |
In this example the oldest bucket is 2. However, the balance of the bucket is negative so the bucket's balance is taken off the next oldest bucket until the bucket's balance is greater than zero. Therefore, the oldest bucket in this example is 1. This makes the customer's credit status 1.
Example 3
Invoice ageing method is By invoice date.
The number of days between each Invoice date and the Run date is determined and the invoices are aged into their appropriate buckets using the table below:
| 0 | Indicates only current invoice |
| 1 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 30 days old or over |
| 2 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 60 days old or over |
| 3 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 90 days old or over |
| 4 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 120 days old or over |
| 5 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 150 days old or over |
| 6 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 180 days old or over |
The following table illustrates this ageing:
| Invoice Number | Invoice Date | Invoice Terms | Invoice Balance | Age | Bucket |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800056 | 12 May 20xx | 30 days | -45.00 | 95 days | 3 |
| 100512 | 8 June 20xx | 7 days | 50.00 | 68 days | 2 |
| 100513 | 8 June 20xx | 30 days | 120.00 | 68 days | 2 |
| 100556 | 18 June 20xx | 30 days | 85.00 | 58 days | 1 |
In this example the oldest bucket is 3. However, the value of the bucket is negative so the bucket's balance is taken off the next oldest bucket until the bucket's balance is greater than zero. Therefore, the oldest bucket in this example is 2. This makes the customer's credit status 2.
Example 4
Invoice ageing method is By invoice due date.
The number of days between each invoice date and the run date is determined and then this figure is reduced by the due days against the terms code attached to the invoice. The invoices are then aged into their appropriate buckets using the table below:
| 0 | Indicates that there are no overdue invoices |
| 1 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 1-30 days overdue |
| 2 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 31-60 days overdue |
| 3 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 61-90 days overdue |
| 4 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 91-120 days overdue |
| 5 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 121-150 days overdue |
| 6 | Indicates at least one invoice which is 151 days or more overdue |
The following table illustrates this ageing:
| Invoice Number | Invoice Date | Invoice Terms | Invoice Balance | Overdue | Bucket |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800056 | 12 May 20xx | 30 days | -45.00 | 65 days | 3 |
| 100512 | 8 June 20xx | 7 days | 50.00 | 61 days | 3 |
| 100513 | 8 June 20xx | 30 days | 120.00 | 38 days | 2 |
| 100556 | 18 June 20xx | 30 days | 85.00 | 28 days | 1 |
In this example the oldest bucket with a positive balance is 3. This makes the customer's credit status 3.
If you selected the option: Consolidate brought-forward customers at month end (Accounts Receivable Setup), then this following example describes how the Balance Brought Forward buckets are affected when a Month end or Year end function is performed.
Example:
The transactions are for a new customer with no history of transactions.
-
Period 1 - Invoice for 150.00 is posted using the AR Invoice Posting program. The cost value is zero.
-
The Invoice amount 150.00 is added to the Current balance 1 field(0 + 150.00 = 150.00).
-
The Invoice amount 150.00 is added to the Month to date sales 1 field(0 + 150.00 = 150.00).
-
The Invoice amount 150.00 is added to the Month to date profit 1 field(0 + 150.00 = 150.00).
-
The Invoice amount 150.00 is added to the Month to date invoice value 1 field(0 + 150.00 = 150.00).
-
The Invoice amount 150.00 is added to the Year to date Sales field(0 + 150.00 = 150.00).
-
The Invoice amount 150.00 is added to the Year to date profit field(0 + 150.00 = 150.00).
-
-
Period 1 - Payment of 25.00 received from customer and processed using Payments and Adjustments program.
-
The Payment amount -25.00 is added to the Current balance 1 field (150.00 + (-25.00) = 125.00).
-
The Payment amount -25.00 is added to the Month to date payment value 1 field (0 + -25.00 = -25.00).
-
-
Period 1 - Month end is executed using the AR Period End program.
-
The Invoice balance (Total of all invoice amounts + total of all transaction payments per client per invoice) is moved to the Current balance 1 field. (150.00 + (-25.00) = 125.00)
-
The Current Balance 1 field is moved to the Current Balance 2 field.
-
The Current Balance 1 field is moved to the Balance brought forward 1 field.
-
Month to date sales 1 field is moved to Month to date sales 2 field.
-
Zero is moved to Month to date sales 1 field.
-
Month to date profit 1 field is moved to Month to date profit 2 field.
-
Zero is moved to Month to date profit 1 field.
-
Month to date invoice value 1 field is moved to Month to date invoice value 2 field.
-
Zero is moved to the Month to date invoice value 1 field.
-
Month to date payment value 1 field is moved to Month to date payment value 2 field.
-
Zero is moved to the Month to date payment value 1 field.
-
The invoice is aged according to the Invoice ageing method selected (Accounts Receivable Setup) and is moved to the Value current invoice field.
-
The Month to date sales 2 field is moved to the Sales value month 1 field.
-
-
Period 2 - Payment of 32.00 received from customer and processed using Payments and Adjustments program.
-
The Payment amount -32.00 is added to the Current balance 1 field (125.00 + (–32.00) = 93.00).
-
The Payment amount (-32.00) is added to the Month to date payment value 1 field (0 + (-32.00) = (-32.00).
-
-
Period 2 - Month end is executed using the AR Period End program.
-
The Current balance 2 field is moved to the Current balance 3 field.
-
The Current balance 1 field is moved to the Current balance 2 field.
-
The Invoice balance (Total of all invoice amounts + total of all transaction payments per client per invoice) is moved to the Current balance 1 field. (125.00 + (-32.00) = 93.00).
-
The Balance brought forward 1 field is moved to the Balance brought forward 2 field.
-
The Current Balance 1 field is moved to the Balance brought forward 1 field.
-
Month to date sales 2 field is moved to Month to date sales 3 field.
-
Month to date sales 1 field is moved to Month to date sales 2 field.
-
Zero is moved to Month to date sales 1 field.
-
Month to date profit 2 field is moved to Month to date profit 3 field.
-
Month to date profit 1 field is moved to Month to date profit 2 field.
-
Zero is moved to Month to date profit 1 field.
-
Month to date invoice value 2 field is moved to Month to date invoice value 3 field.
-
Month to date invoice value 1 field is moved to Month to date invoice value 2 field.
-
Zero is moved to the Month to date invoice value 1 field.
-
Month to date payment value 2 field is moved to Month to date payment value 3 field.
-
Month to date payment value 1 field is moved to Month to date payment value 2 field.
-
Zero is moved to the Month to date payment value 1 field.
-
The invoice is aged according to the Invoice ageing method selected (Accounts Receivable Setup) and is moved to the Value current invoice field.
-
The Sales value month 1 field is moved to the Sales value month 2 field.
-
The Month to date sales 2 field is moved to the Sales value month 1 field.
-
-
Period 3 - Payment of 60.00 received from customer and processed using Payments and Adjustments program.
-
The Payment amount -60.00 is added to the Current balance 1 field (93.00 + (–60.00) = 33.00).
-
The Payment amount -60.00 is added to the Month to date payment value 1 field (0 + (-60.00) = -60.00).
-
-
Period 3 -Month end is executed using the AR Period End program.
-
The Current balance 2 field is moved to the Current balance 3 field.
-
The Current balance 1 field is moved to the Current balance 2 field.
-
The Invoice balance (Total of all invoice amounts + total of all transaction payments per client per invoice) is moved to the Current balance 1 field. (93.00 + (-60.00) = 33.00)
-
The Balance brought forward 2 field is moved to the Balance brought forward 3 field.
-
The Balance brought forward 1 field is moved to the Balance brought forward 2 field.
-
The Current Balance 1 field is moved to the Balance brought forward 1 field.
-
Month to date sales 2 field is moved to Month to date sales 3 field.
-
Month to date sales 1 field is moved to Month to date sales 2 field.
-
Zero is moved to Month to date sales 1 field.
-
Month to date profit 2 field is moved to Month to date profit 3 field.
-
Month to date profit 1 field is moved to Month to date profit 2 field.
-
Zero is moved to Month to date profit 1 field.
-
Month to date invoice value 2 field is moved to Month to date invoice value 3 field.
-
Month to date invoice value 1 field is moved to Month to date invoice value 2 field.
-
Zero is moved to the Month to date invoice value 1 field.
-
Month to date payment value 2 field is moved to Month to date payment value 3 field.
-
Month to date payment value 1 field is moved to Month to date payment value 2 field.
-
Zero is moved to the Month to date payment value 1 field.
-
The invoice is aged according to the Invoice ageing method selected (Accounts Receivable Setup) and is moved to the Value 30 days field.
-
The Sales value month 2 field is moved to the Sales value month 3 field.
-
The Sales value month 1 field is moved to the Sales value month 2 field.
-
The Month to date sales 2 field is moved to the Sales value month 1 field.
-
-
It is strongly recommended that you take a backup of your data before processing a Month end, a Year end or a Purge.
Electronic Signatures provide security access, transaction logging and event triggering. This enables you to increase control over your system changes.
Access to the following eSignature transactions within this program can be restricted at Operator, Group, Role or Company level. You configure this using the Electronic Signatures program.
| eSignature Transaction | Description |
|---|---|
| AR Month-end performed |
Controls access to the Month-end processing function in the AR Period End program. |
| AR Year-end performed |
Controls access to the Year-end function in the AR Period End program. |
| AR Purge performed |
Controls access to the Purge processing function in the AR Period End program. |
| AR Balance function performed |
Controls access to the Balance processing function in the AR Period End program. |
Inserting Application Help
You would typically follow this procedure to display help for the current program in a customized pane that can be pinned to the program window.
Information includes step-by-step instructions for the various functions available within the program, including a brief overview of what the program does, what setup options are required and how to personalize the program.
-
Open the program for which you want to insert application help into a customized pane.
This functionality is only available for a program that has panes.
-
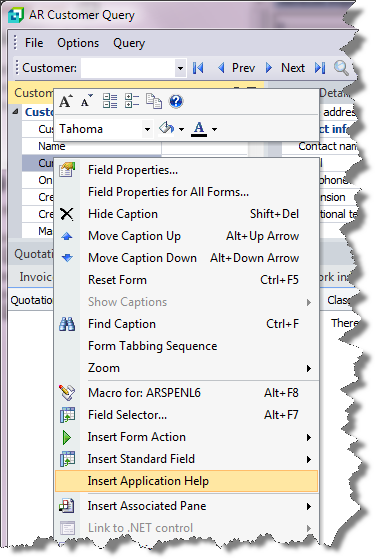
Right-click any form field.
You can also click the triangle menu icon that appears in the title area of a pane.
-
Select Insert Application Help from the context-sensitive menu.
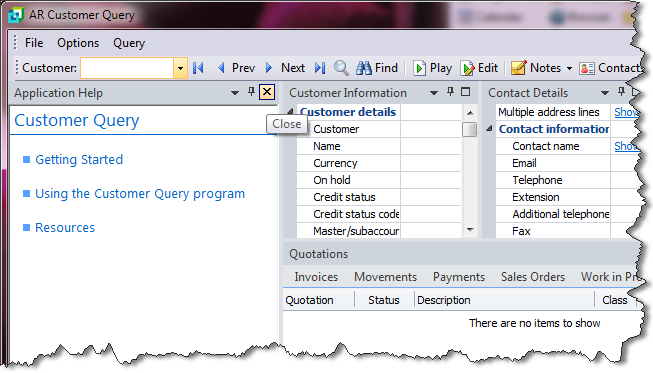
The application help appears in a pane within your program. You can reposition the pane using the docking stickers or pin it to the program window.
Removing the Application Help pane
If you no longer want to display application help in a pane for your current program, you can simply remove it.
-
Select the Close icon in the right-hand corner of the application help pane.
-
Confirm that you want to delete the pane.